Hold Em Hands
6+ Hold’em is a popular ‘short deck’ poker format that plays much like Texas Hold’em, but with a few exciting differences:
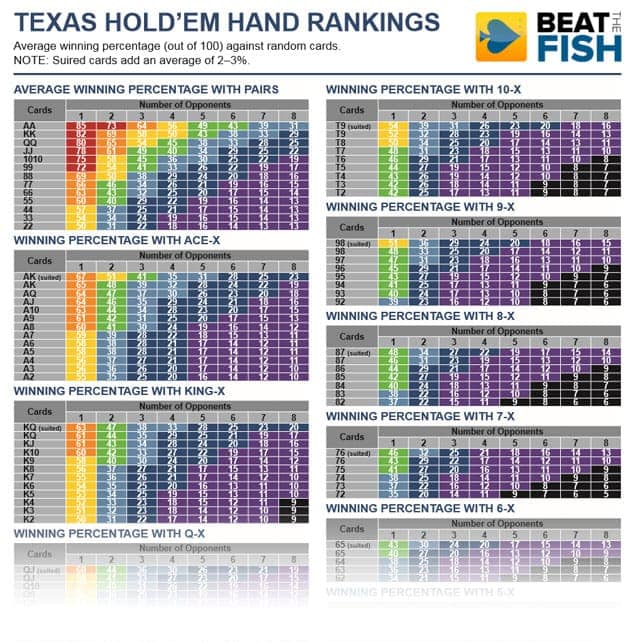
What’s the Best Hold’em Hand? If you’re pre-flop the answer is easy: pocket aces. Outside of those. Mediocre hands are all a jumble of mediocre winning percentages. Some of the most common hands that many Hold’em players stick with like KQ, J-10, or Q-J all have similar middling winning percentages.
- All cards lower than a six are removed from the deck
- Everyone posts an ante and only the button posts a blind – known as the ‘button blind’
- A flush beats a full-house
Available in cash games, exclusively at PokerStars, 6+ Hold’em is your chance to play an action-packed variant loved by high-stakes players around the world.
Let’s face it – fives, fours, threes, and twos got in the way a little bit in regular Holdem. They were consistent contributors to dry boring flops, blank turns, and no one ever making a hand. 6+ Hold’em (known conventionally as ‘Short Deck’) has been taking the poker world by storm and giving jaded long-term players a fresh breath of life as they gamble it up in this wild format of the game played with a 36-card deck. Six Plus is exactly as it sounds. There is no card in the deck below a six. As you can imagine, this leads to a lot less discoordination and makes it far easier to make a strong hand. When I first saw this game, I recall my first thought being:
‘Wait a second…it’s almost impossible not to make a straight!’
While this is a huge exaggeration. I think it captures the instinctive reaction of most players. Regular Holdem players must adapt quickly in 6+ Hold’em, migrating from a world where good hands are relatively rare, to one where they come along much more frequently. We shall get into the strategic effects of this shift in a future article. Today’s job is to get our heads around what hand rankings and rules have changed and why these changes were necessary to make 6+ Hold’em the harmoniously enjoyable game that it has become.
Blind & Antes
6+ Hold’em uses a ‘button blind’ structure: every player posts an ante, and the player seated at the button position is the only one who posts a blind – meaning there is only one blind per hand, rather than traditional small/big blind format.
The action starts with the player seated to the left of the button. Each hand then plays out according to Texas Hold’em rules, with pre-flop, flop, turn and river betting rounds.
If you’ve played Texas Hold’em games before, the rules of 6+ Hold’em are easy to follow.
Hand Rankings
The table below illustrates how the hand rankings have changed in 6+ Hold’em to accommodate the shorter deck:
The Top Hands
There is no change at the very top of the hand ranking chart. While you will make a straight flush and a royal flush more often in 6+ Hold’em than in Holdem, it is still very hard to make these hands relative to the other hands. Four of a Kind is a hand you will see much more often than in Holdem since there are now 9 ranks of card instead of thirteen but is still rare compared with other 6+ Hold’em holdings.
Flushes vs. Boats
The main change to the hierarchy is that Flushes now beat Full Houses (boats). This makes sense and to see why think of it this way.
In regular Holdem, there are four 9s in the deck, but there are also four of twelve other ranks of card. One in thirteen cards is a nine in regular Holdem. In 6+ Hold’em, there are only nine ranks of card and so one in nine cards is a 9. If you are dealt 99, any card in the deck goes from having a 2/50 = 4% chance of being a 9 to having a 2/34 = 6% chance. In 6+ Hold’em, it is 50% easier to find those set making cards. In fact, in 6+ Hold’em you will fail to flop a set (32/34 x 31/33 x 30/32) = 83% of the time. This means that we flop a set 17% of the time! After we have done the hard part, and hit one of our two cards to make a set, it is much easier for the board to then pair since sixteen of the cards that would prevent it from pairing in regular holdem (the deuces through fives) do not exist. Those cards really did spoil all the fun.
As for flushes, they are sadly no easier to make and come along less often than a full house does. While there are less ranks of cards in the 6+ Hold’em deck, there are still the same number of suits. Had we also removed all of the diamonds from the deck, we would have made flushes more likely. As it is, every card still has a one in four chance of being a spade (13/52 = 9/36).
One thing that has changed about flushes in short deck is that when a you hold a card that blocks an opponent from making a flush, you will block a greater portion of his possible flush cards. The board is J♣8♣6♣10♠Q♥ and we hold A♥K♣. In regular Holdem, we would remove one of ten remaining clubs, leaving Villain with nine clubs to instead of ten to form a flush. In other words, there are 10% less clubs in the deck for him to make a flush with when we hold this blocker. In 6+ Hold’em, there were only six possible clubs and we reduce this number to five due to our K♣ blocker. We have now made it 17% harder for Villain to hold a flush by removing a sixth of the clubs in the deck. Blockers matter more in 6+ Hold’em in just about every way due to the smaller deck, not just when it comes to blocking flushes.
Straights vs. Trips
While it is easier to flop three of a kind in 6+ Hold’em than it is to flop a straight, it is easier to make a straight by the river. There are only 9 ranks of cards remaining in the deck so if the board doesn’t double-pair, there will be straights everywhere. A board like K♠J♠10♣8♥6♥ is scary at the best of times in regular Holdem. In 6+ Hold’em, there are no deuces through fives to dilute the number of straights in each player’s range. The result is that it is incredibly easy to hold a straight in 6+ Hold’em. Pre-flop you will be dealt [97, Q9, AQ] 48/630 times. In Regular Holdem you will be dealt these hands 48/1326 times. While there are some versions of short deck Holdem where three of a kind beats a straight, this is not the case in 6+ Hold’em and so connected cards are very powerful. This format of the game encourages action by providing an incentive to play connected cards, which come along very frequently.
We should also note that there is a rather unconventional looking straight available in 6+ Hold’em. A6789 is a low straight in 6+ Hold’em just as A2345 is a low straight in regular Holdem. Look out for this one, it can really tak you by surprise if you are not careful.
Conclusion
6+ Hold’em is a different game. Some of the rules are very different, but as we have seen, these adaptations have been necessary to ensure that the game is fair and balanced. Now that we are acquainted with the different hand rankings and hand formation rules, it is time to get stuck into some strategy. In my next article on 6+ Hold’em, I will be discussing pre-flop hand selection.
Join us on our Discord channel.
NL Hold’em Starting Hand Charts
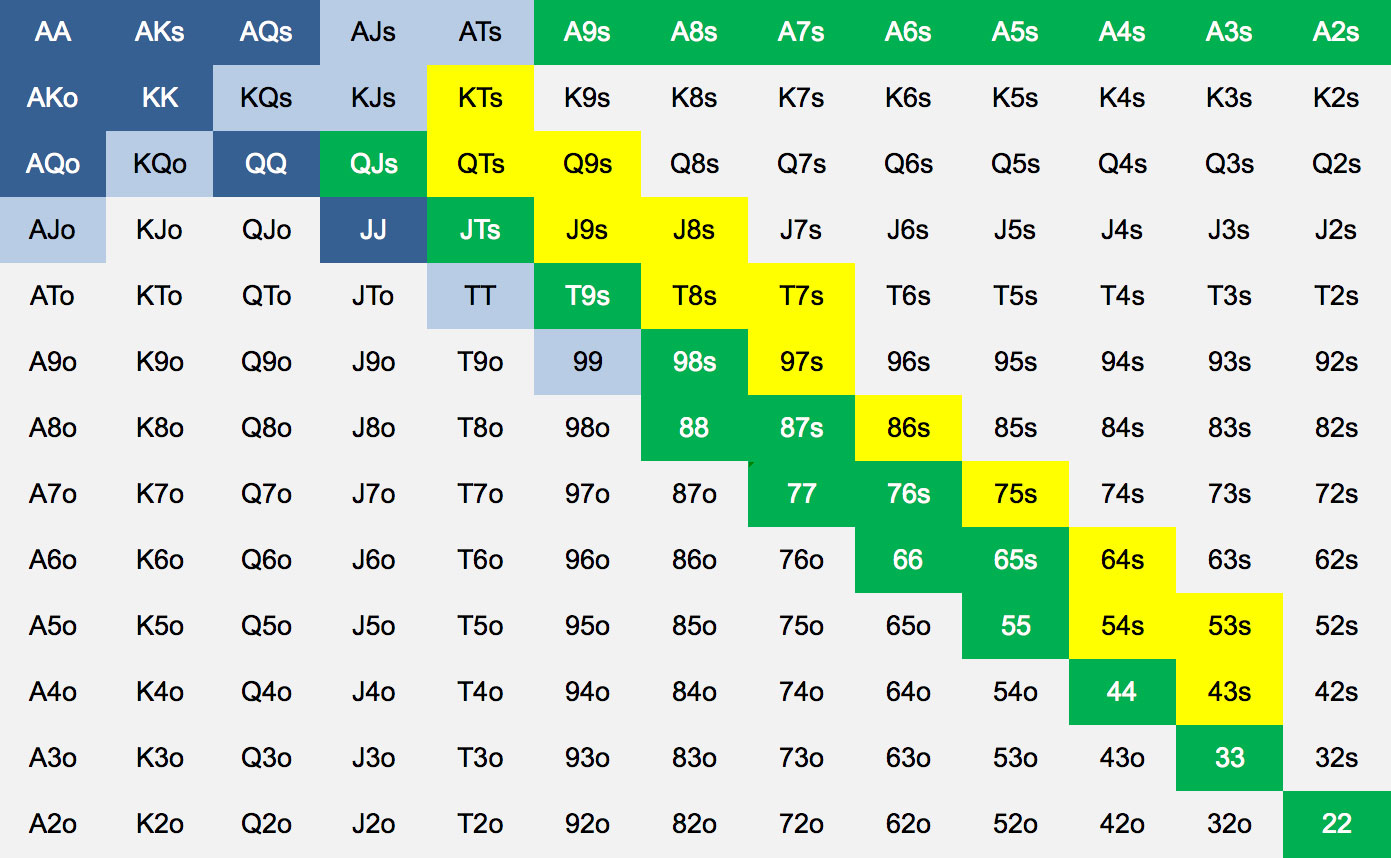
One aspect of the game of No-Limit Hold’em that causes beginning players much grief is deciding which hands to play and which hands to dump. NL Hold’em is much more difficult than Limit Hold’em because the value of a hand depends on so many factors other than just the cards in your hand. Despite this difficulty, our coaches believe that following some general guidelines and adjusting from these is a better solution than having no guidelines at all. Given that well over half of your profitability in NL Hold’em is based on hand selection alone, we have developed these charts to help you better determine whether to play or fold.
There are no perfect No-Limit starting hand charts. That is because there are many factors that affect your decision, and charts cannot account for all of them. Some of these include:
- The size of your opponent's stacks.
- How loose or tight, passive or aggressive, your opponents are.
- Where these opponents are located at the table – for example, does an aggressive player still have to act after you?
- Your image at the table – for example, how tight or tricky you are perceived.
That being said, these charts will serve you well in most typical low-stakes No-Limit cash games, such as games with blinds of $1/$2, and home games. These games typically have several loose players at the table, and good opportunities for winning big pots with suited connectors and pocket pairs. With practice, you will be able to be a consistently winning player with these charts as a starting point. As you improve, you'll find yourself making adjustments to these charts based on the factors listed above, and more.
AGAIN: These charts are a good starting point for beginners. Specifically, Chart #1 recommends a significant amount of limping. This is great in loose, passive games but less often seen in tougher games. You’ll find other training material on Advanced Poker Training that may recommend a more aggressive approach for more experienced players.
Note: It would be a serious mistake to apply these hand charts before reading the Frequent Asked Questions first.
CHART #1 ‐ LOOSE, PASSIVE GAME (OFTEN 4-5 LIMPERS PER HAND)
NO ONE HAS RAISED YET
- Raise Always
- Call from Early Position, otherwise raise
- Call always
- Call from Middle or Late Position if the conditions are right (see Frequently Asked Questions)
Winning Hands In Texas Hold'em

CHART #2 ‐ TIGHTER GAME (FEWER LIMPERS) OR MORE AGGRESSIVE GAME
NO ONE HAS RAISED YET
- Raise Always
- Call from Early Position, otherwise raise
- Call (or Raise) from Middle or Late Position if the conditions are right (see Frequently Asked Questions)
CHART #3 ‐ THERE HAS BEEN A SINGLE RAISE
(3‐5 TIMES THE BIG BLIND) BEFORE YOU

- Re‐Raise Always
- Call from Early Position, otherwise re‐raise
- Call always
- Call from Middle or Late Position if the conditions are right (see Frequently Asked Questions)
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Texas Holdem Hands
For the hands in yellow, what do you mean when you say to play these hands if the conditions are right? The hands in yellow are speculative hands. They should always be folded from Early Position. From other positions, they can be profitable given the right conditions. Some of the questions to ask yourself:
- Are there other players who have called so far (the more, the better)?
- Are the players who have called playing poorly after the flop? Will they pay me off if I hit something?
- Is there an aggressive player still to act behind me (you might get raised and have to fold)?
- If there has been a raise and no other callers, what chance do I have of using my position after the flop to win the hand even if I don't improve (Chart #3 only)?
Why does Chart #2 say to sometimes raise with the hands in yellow, but Chart #1 does not? We have different goals in mind. Using Chart #1, we want to call to encourage additional players to enter the pot. These hands will be immensely profitable when our loose, passive opponents enter the hand, and get trapped when we flop a set, or make a well-disguised straight. When using Chart #2, however, we want to size up the opponents still to act. If they are tight, we can raise. Sometimes, we'll pick up the blinds. Other times, our pre-flop aggression will allow us to take down the pot on the flop.

What's the difference between AKs and AKo? AKs means an Ace and King of the same suit. AKo means an Ace and King of different suits.
What are early, middle, and late position? Early Position is generally the first 2 (in a nine player game) or 3 (in a ten player game) positions after the blinds. Late Position is the “cutoff” position (to the right of the dealer), and dealer button positions. Middle Position is everything in between.
How much should I raise? As a general rule, raise 3 to 4 times the big blind, plus 1 extra big blind for every player who has called before you. So if there are 2 callers already, raise between 5 and 6 times the big blind.
What if someone raises after I call? Whether you call the raise depends on how much money the raiser has for you to win, how many other players are involved, and what type of hand you have. As a general rule, if you have a pocket pair, lean towards calling. If there are a lot of other players (and therefore a big pot), lean towards calling. In general, fold suited connectors from early position. Fold hands like KQ that don't play well against a raiser.
How do I play from the blinds? From the small blind, play the same hands you would play from late position, plus a few more. But don't call with junk hands like T5o, just because it is “cheap”. From the big blind, if there is a raise to you, play like you would if you had already called from early position.
The chart says to fold KQo to a raise. Really? Yes, this hand performs very poorly against typical raising hands. Against AK, AQ, AA, KK, QQ, you are a big underdog. Other typical raising hands like JJ, TT, 99, AJs, are slightly ahead of you as well. The only time you might call or re-raise is from late position, if the opener was in middle or late position, indicating they might have a wider range of hands.
I was told to fold AJo from Early Position, why do you say to call with it? Folding AJo is not a bad idea in many games. We included it because, at low stakes tables (even tight or aggressive ones), the players are often playing badly enough after the flop that it can be profitable. We used data from millions of hands of low-limit poker to analyze this. The same could be said for KQo, ATs, and KJs – you can make a small profit in the long run at most low-stakes games, but folding would be perfectly acceptable from early position.
Can I use these charts in a NL Hold'em tournament? The charts would be best applicable to the early stages of a NL tournament, when everyone has a deep stack. In the middle and later stages, they should not be used.